Table of Contents
- – Understanding EMDR Treatment: Exactly How It W...
- – The 8 Phases of EMDR Therapy
- – Sylvia Lagosky
- – Accelerated Resolution Therapy: Fast-Track Tra...
- – EMDR Intensives: Concentrated Recovery in Comp...
- – Dealing With Stress And Anxiety with EMDR and ART
- – Somatic Parts of Trauma-Focused Treatment
- – Choosing In Between EMDR and ART for Your Requ...
- – What to Expect from Trauma-Focused Therapy
- – Finding Qualified EMDR and ART Specialists
Injury doesn't adhere to a predictable timeline for recovery. Standard talk therapy aids many individuals process difficult experiences, but some memories remain stubbornly immune to conventional approaches. Eye Motion Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) and Accelerated Resolution Treatment (ART) have actually become powerful alternatives for individuals whose trauma signs continue despite years of therapy. These evidence-based treatments supply paths to relief that can feel extremely faster than standard techniques, in some cases generating substantial changes in just a couple of sessions.

Understanding EMDR Treatment: Exactly How It Works
EMDR intensivesEye Activity Desensitization and Reprocessing represents a paradigm shift in trauma treatment. Developed by Francine Shapiro in the late 1980s, EMDR therapy operates the concept that distressing memories come to be "" stuck"" in the mind's processing system, keeping their emotional charge and causing power long after the initial event. Unlike typical treatment that depends largely on spoken handling, EMDR makes use of reciprocal excitement-- normally eye motions, taps, or tones-- to promote the brain's natural healing systems.
The procedure entails remembering terrible memories while concurrently participating in reciprocal excitement. This twin interest appears to enable the brain to reprocess stuck memories, decreasing their psychological strength and incorporating them into more comprehensive life narratives. Customers usually define the experience as viewing a motion picture of their injury that slowly loses its power, transforming from a natural experiencing again right into a more remote recollection.
What makes EMDR especially compelling is the extensive research study sustaining its performance. The Globe Health Organization, American Psychiatric Association, and Division of Veterans Affairs all recognize EMDR as an evidence-based treatment for trauma and PTSD. Researches regularly demonstrate that EMDR generates outcomes equivalent to or much better than typical trauma-focused cognitive behavioral treatment, often in fewer sessions.
The 8 Phases of EMDR Therapy
EMDR therapy complies with a structured eight-phase protocol that ensures extensive treatment. The process begins with history-taking and therapy planning, where therapists recognize target memories and assess customer preparedness for injury processing. This preparation stage shows essential-- therapists instruct basing methods and dealing abilities that clients can use if handling comes to be overwhelming.
The analysis phase involves identifying specific memories, negative ideas connected with those memories, and desired favorable ideas. A memory of an automobile accident may carry the negative cognition "" I'm not safe,"" which treatment aims to change with "" I survived and I'm risk-free currently."" Customers rank their distress degrees and idea strength, providing quantifiable markers of development throughout treatment.
Desensitization-- the heart of EMDR-- involves remembering the target memory while complying with the therapist's moving hand or engaging with reciprocal faucets or audios. Processing continues until the memory's emotional charge decreases considerably. Installment enhances the favorable idea, while body check ensures no residual physical tension remains. Closure and reevaluation stages total each session and analyze progress gradually.
Sylvia Lagosky
Accelerated Resolution Therapy: Fast-Track Trauma Processing
Accelerated Resolution Therapy improves EMDR's foundation while introducing one-of-a-kind components made to accelerate recovery. Created by Laney Rosenzweig in 2008, ART shares EMDR's usage of eye movements however integrates imagery rescripting techniques that permit customers to psychologically "" change the network"" on stressful memories. This method usually creates remarkable outcomes in remarkably brief durations-- commonly one to five sessions.
The increased nature of ART comes from its direct targeting of sensory memories. Instead of extensive verbal processing, ART focuses on changing troubling pictures with neutral or favorable ones while retaining accurate memory of events. A veteran may keep in mind the realities of a fight experience without the intrusive nightmares and flashbacks that previously come with those memories.
ART treatment shows specific effectiveness for single-incident injuries like accidents, assaults, or medical procedures. The method enables customers to maintain the material of their injury personal if wanted-- therapists do not need comprehensive spoken summaries to help with efficient processing. This feature charms to people hesitant to vocally recount painful experiences or those worried about confidentiality in particular expert contexts.
EMDR Intensives: Concentrated Recovery in Compressed Timeframes
Typical once a week therapy sessions work well for many individuals, yet some situations ask for even more extensive treatment. EMDR intensives condense therapy right into longer, a lot more constant sessions-- in some cases complete or half-day appointments over successive days. This layout permits much deeper handling without the disturbance of going back to life between common 50-minute sessions.
Intensives especially benefit individuals taking care of particular stressful occasions, prep work for major life changes, or those who have actually plateaued in typical therapy. The concentrated format develops energy that can appear resistance and allow processing that might take months in regular sessions. Travel from out of state becomes possible when therapy presses into a week or long weekend as opposed to calling for months of normal consultations.
Durability Currently and comparable specialized practices usually structure intensives around private requirements, integrating EMDR with complementary techniques like somatic therapy or mindfulness methods. The intensive format needs careful preparation and follow-up assistance to ensure customers can integrate their processing and preserve gains after returning home.
Dealing With Stress And Anxiety with EMDR and ART
While EMDR and ART developed their online reputations dealing with trauma and PTSD, both approaches demonstrate performance for stress and anxiety conditions even without clear stressful beginnings. Panic condition, social anxiety, and generalized anxiousness commonly have origins in earlier experiences that may not certify as capital-T injury but however produced long lasting patterns of fear and evasion.
EMDR targets the memories, situations, and triggers that gas existing anxiety. Somebody with social anxiety may refine very early experiences of embarrassment or rejection that established ideas about being evaluated or poor. As these memories lose their psychological charge through bilateral excitement, contemporary stress and anxiety symptoms typically lessen significantly.
ART's fast handling makes it specifically appealing for people whose stress and anxiety hinders work, relationships, or lifestyle. The prospect of purposeful relief within a handful of sessions encourages people that might otherwise delay looking for treatment. Both modalities offer hope that anxiety does not need years of monitoring-- it can possibly solve via targeted reprocessing of the experiences that established distressed patterns.
Somatic Parts of Trauma-Focused Treatment
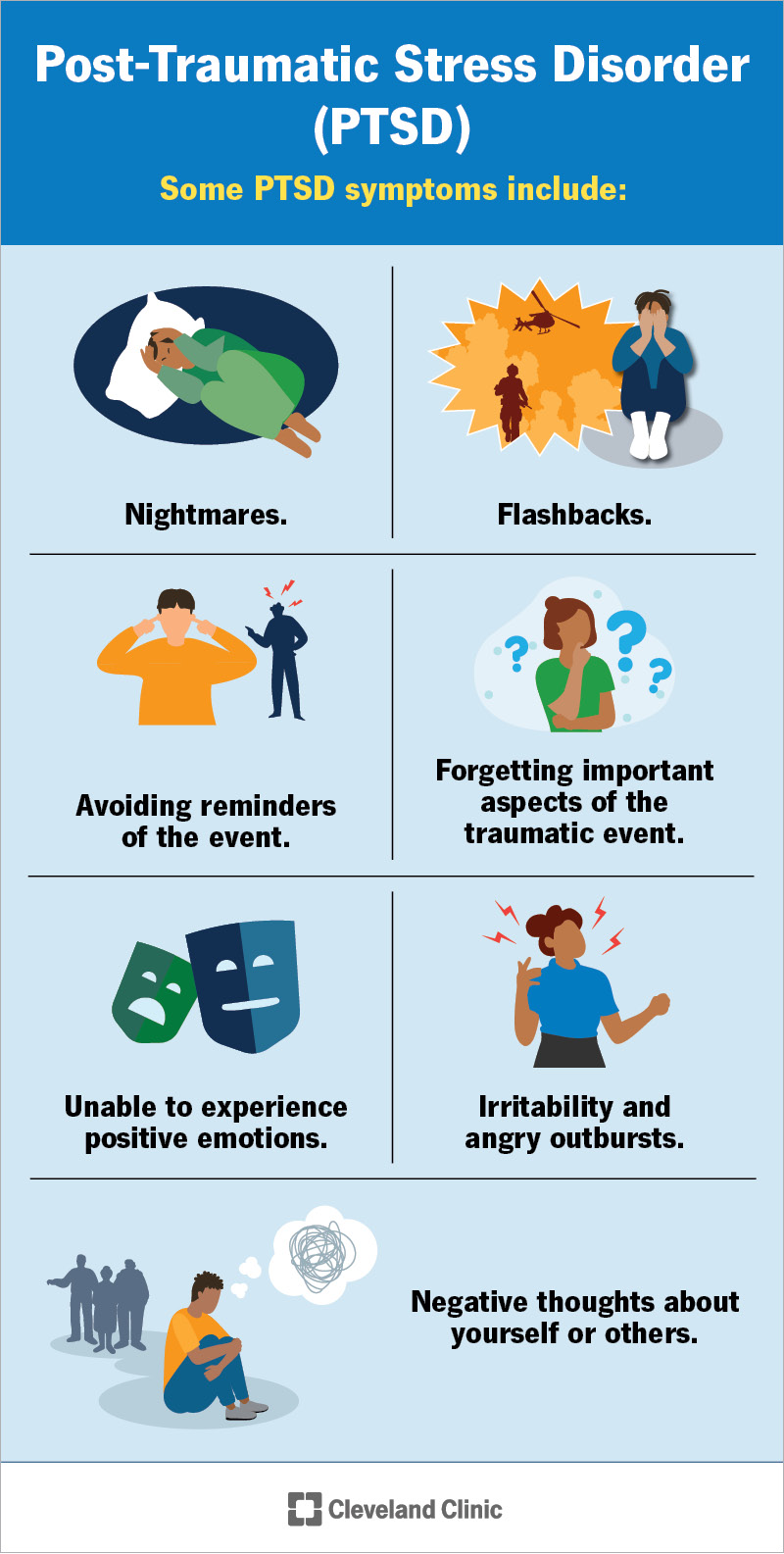
Both EMDR and ART identify that injury lives in the body as much as the mind. Distressing memories commonly materialize as physical sensations-- rigidity in the upper body, nausea or vomiting, muscle tension-- that persist even when the original threat has passed. Effective injury therapy addresses these somatic elements instead than focusing exclusively on ideas and emotions.
During EMDR processing, customers track physical feelings as memories shift. Stress could at first boost before launching, or brand-new feelings could arise as handling proceeds. Therapists direct interest to these body experiences, enabling them to educate and progress the reprocessing work. The body scan phase especially ensures that no residual physical holding patterns remain after cognitive and psychological processing finishes.
This somatic awareness proves specifically essential for complicated injury, where hypervigilance and physical reactivity ended up being embedded survival responses. Finding out to track and launch body-based trauma reactions assists clients recover a feeling of safety and security and presence that trauma had stolen.
Choosing In Between EMDR and ART for Your Requirements
Both EMDR and ART supply powerful injury treatment, however specific aspects could make one more suitable for your particular circumstance. EMDR's extensive research base and eight-phase framework attract individuals that value completely verified methods and value clearly specified treatment methods. The method's adaptability enables adjustment for complicated trauma, accessory injuries, and ongoing difficult situations.
ART's rapid results make it optimal for single-incident injury, details fears, or circumstances needing fast resolution. The privacy managed by minimal verbal disclosure benefits some customers, while others might miss the handling that comes from talking through experiences. Some professionals integrate both approaches, using ART for discrete memories and EMDR for more complicated presentations.
What to Expect from Trauma-Focused Therapy
Starting EMDR or ART needs readiness to engage with excruciating memories, even as the processing itself lowers their effect. Initial sessions concentrate on building resources and ensuring appropriate coping abilities exist for managing possible distress. Quality trauma specialists never ever rush into processing prior to establishing security and stabilization.
The experience of bilateral stimulation differs-- some individuals hardly observe eye motions or taps, while others discover them initially unusual or distracting. Most customers adjust swiftly, and the reciprocal component quickly discolors right into background awareness as processing takes spotlight. In between sessions, new insights, memories, or feelings might surface as the brain continues integrating material.
Development does not always follow a straight course. Some sessions produce significant changes while others feel slower or more tough. Trusting the procedure and keeping commitment with varying experiences permits the full advantage of these approaches to arise. Follow-up sessions assess whether processing holds and attend to any kind of remaining targets or brand-new product that surfaces.
Finding Qualified EMDR and ART Specialists
Not all therapists offering EMDR or ART have equivalent training or experience. Fundamental EMDR training needs completion of approved programs, but additional consultation, progressed training, and managed technique different competent professionals from absolutely competent ones. Look for specialists licensed by EMDR International Organization (EMDRIA) or that have actually finished substantial monitored hours beyond fundamental training.
For ART, accreditation needs details training in the procedure and supervised method. The therapy's relative newness compared to EMDR implies fewer specialists supply it, yet expanding research study support proceeds increasing accessibility. Specialized methods like Resilience Now frequently focus specifically on trauma-informed techniques, ensuring personnel competence in these strategies.
Throughout examinations, inquire about specific training, years of exercise with the technique, and sorts of trauma commonly dealt with. A specialist's convenience and self-confidence with the approach matters considerably-- efficient EMDR and ART require adaptability to adapt procedures while maintaining integrity to core concepts. The appropriate match combines technological know-how with the relational skills that make all treatment effective.
Table of Contents
- – Understanding EMDR Treatment: Exactly How It W...
- – The 8 Phases of EMDR Therapy
- – Sylvia Lagosky
- – Accelerated Resolution Therapy: Fast-Track Tra...
- – EMDR Intensives: Concentrated Recovery in Comp...
- – Dealing With Stress And Anxiety with EMDR and ART
- – Somatic Parts of Trauma-Focused Treatment
- – Choosing In Between EMDR and ART for Your Requ...
- – What to Expect from Trauma-Focused Therapy
- – Finding Qualified EMDR and ART Specialists
Latest Posts
Cultivating Emotional Regulation for Long-Term Success
How Current Executive Function Assessment Differs
Addressing Concerns About Mental Health Care
Navigation
Latest Posts
Cultivating Emotional Regulation for Long-Term Success
How Current Executive Function Assessment Differs
Addressing Concerns About Mental Health Care